Environmental management
In 2011 we reaffirmed our main commitment of identifying, assessing, and controlling our activities’ environmental impacts, as well as those of our products and services, in all stages of their life cycle. In the Structural Project for the Environment and Communities, we have decided to give a new look to our social and environmental management by closing our environmental gaps and transforming our management to ensure an excellent performance in the future.
In addition, as a mining company we recognize the importance and place a strong emphasis on the responsible use of natural resources, particularly water and energy, and of managing industrial waste and emissions properly.
For the purpose of comparing all the indicators in this chapter, copper production in 2011 reached 1,617 thousand fine metric tons (fmt), taking only the Codelco divisions into account. It’s important to bear in mind that this is the greatest production recorded in the history of the company.
Resource Use
WATER
Water is a strategic resource for mining operations and projects, and Codelco constantly strives to make management more efficient in terms of withdrawal, use and recirculation to ensure its sustainable use.
To achieve these challenges, we have developed a Corporate Strategy for Water Resources, which operates through a Master Plan for Water Resources and various implementation plans for the divisions, allowing timely feedback on water withdrawal to the authorities.
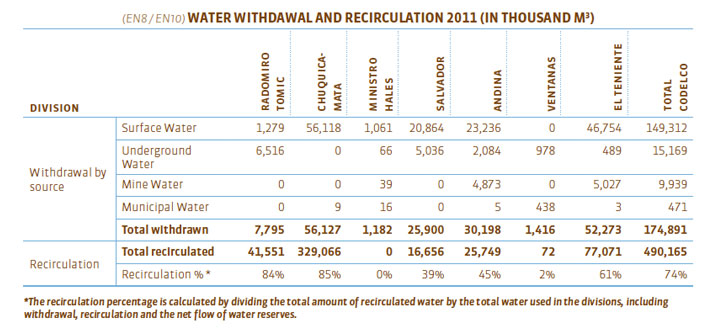
During 2011, we withdrew 174,891 thousand m3 of water from different sources, either for use in operations or for storing for future uses. The total withdrawn this year was higher than in 2010 (by 17,034 thousand m3) as was our recirculation rate, which increased by 1%, maintaining, our efficiency levels in the management of this resource, considering that copper production in 2011 was 2% greater than in 2010.
![]()
In line with our commitment to the
transparent and responsible management
of water resources, at the end of
this year we began the search for alternative
water withdrawal methods that
will help us to be increasingly efficient
and sustainable, especially in the northern
part of the country where water is a
limited resource. For this reason, we are
exploring the desalination of sea water
to lower our traditional consumption of
water and thus lower the pressure for its
use in places where availability is very
limited.
Wastewater
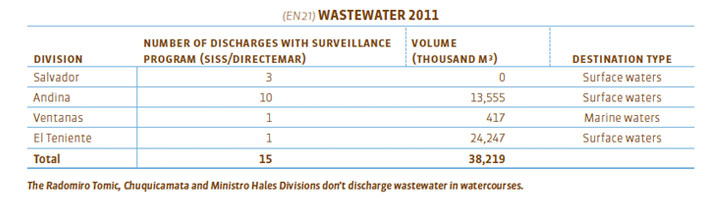
Since the implementation of the Corporate Guideline for Water Resources and Wastewater, we have dedicated our efforts to reducing wastewater and its potential impacts on the environment, reducing our effluents from 25 in 2009 to 15 in 2011, of which four did not present discharges.
Much of the water used in the production process is treated and then re-entered for use in this process cycle. Wastewater, in the end, is the fraction of water which is not reused which is discharged into surface waters (river, stream, etc.) or into the sea.
The authority that regulates compliance with wastewater regulations is the Superintendence of Health Services (SISS), and in the case of effluents to marine waters, the National Marine Authority (Directemar), through Supreme Decrees 90, and 80 in the case of the Carén dam in the El Teniente Division.
During 2011 we maintained our 15 points of wastewater discharge, however the volume discharged was 36% below 2010. This significant decrease may be related to two factors specific to this year. The first is that the El Salvador Division did not discharge wastewater during 2011, due to a significant improvement of water recirculation in its production processes. Secondly, this year was less rainy than the previous one, which also meant a decrease in discharges caused by an overflow of dams and channels.
ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND GREENHOUSE GASES
We have focused on increasing the energy efficiency of processes through better management of resources and equipment and, in addition, we have considered incorporating the use of renewable energy. With this, we seek to contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change.
Codelco Energy Efficiency Plan
(EN5) Energy saved due to conservation and efficiency improvements. During 2011, all Codelco divisions committed their efforts to energy efficiency management, and carried out monthly monitoring of the intensity of their consumption levels. Each division has agreed to a group of energy intensity indicators, accounting as a whole for more than 80% of the energy consumption in Codelco.
In 2011, the energy use intensity indicator reached a value of 27.4 giga joules per fmt (GJ/fmt), lower than that recorded in 2010, which is a measure of the efficiency achieved through a set of initiatives developed during the productive processes and services.

![]()
Days for the dissemination of good
practices in energy efficiency
Throughout several days, the divisions
got to know the projects and initiatives
developed in other work sites of the
Corporation. The central themes were
heat recovery in the smelters and the application
of energy efficiency principles
in electrolytic refineries.
Our consumption
The direct energy consumption in Codelco corresponds to oil and its derivatives, natural gas and coal, and the indirect consumption is related to the electrical power used, from the Central (SIC) and North (SING) Grid Systems. Furthermore, in the Chuquicamata, Salvador, Andina and Ventanas Divisions, there is small scale power self-generation, for own consumption.
During 2011, the total consumption of direct and indirect energy was 45.04 petajoules (PJ), equivalent to 12,511 gigawatts-hour (GWh), slightly higher than consumption in 2010. 53% of this consumption is indirect.
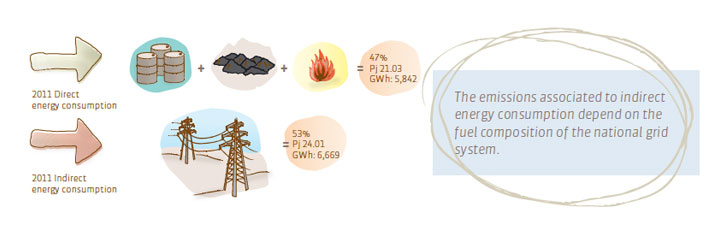
The fuel most used by Codelco in direct consumption is oil and its derivatives (80%), followed by natural gas (19%). The remaining 1% corresponds to coal and other fuels.
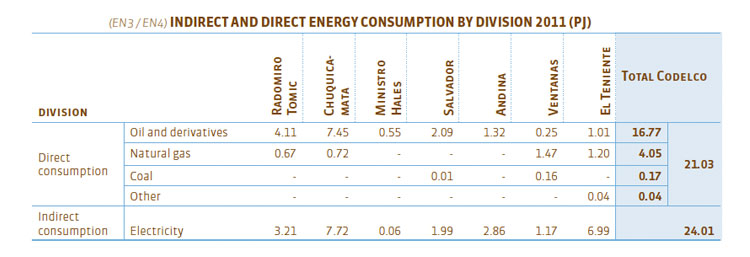
Regarding indirect consumption from the national grid, in 2011 the Corporation consumed 8% of SIC’s power and 19% of SING’s, the latter being 4% less than in 2010.
Greenhouse gas emissions
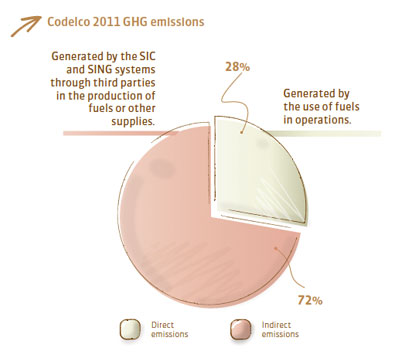
(EN18) Initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reductions achieved There are two types of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with the consumption of energy: direct emissions and indirect emissions. The latter correspond to those emitted by the interconnected SIC and SING grids, and make up 72% of the total emissions associated to Codelco’s production process.
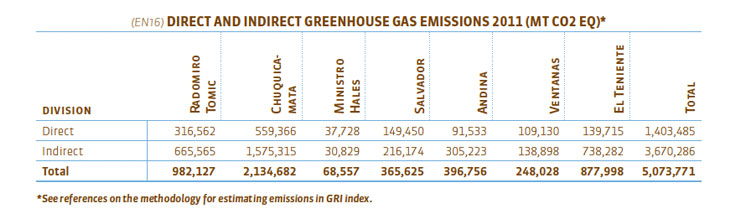
(EN18) Initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reductions achieved. During 2011, we continue to explore alternative energy sources, and we hope to be able to realize some projects in the medium term.
RAW MATERIALS
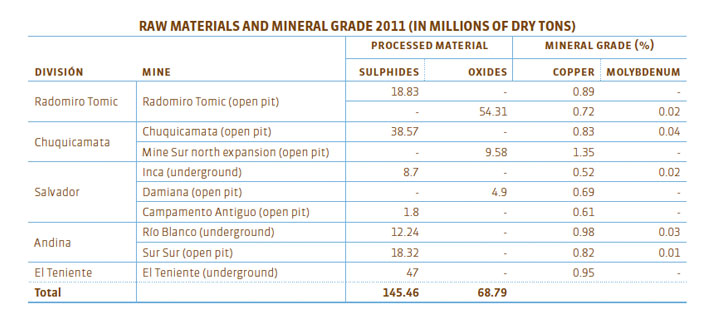
(EN1) Materials used, by weight or volume. The basic raw material used by Codelco in its processes is mineral rock bearing copper and other metals. During 2011 we processed a total of 213.19 million dry tons of mineral rock to obtain copper and molybdenum.
Semi-elaborated materials
(EN1) Materials used, by weight or volume. In addition to mineral rock, we process various semi-elaborated materials procured from external sources, either from another division or from a supplier company.
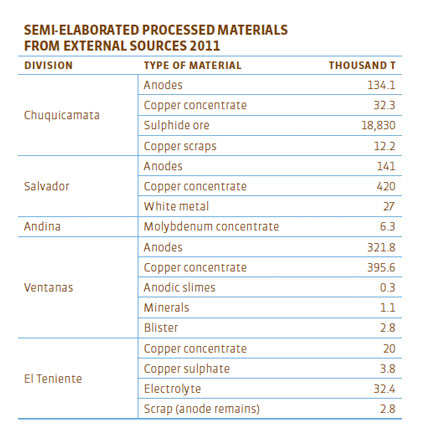
![]()
Valued Materials
“Valued material” is waste from other
companies that is used as supply in our
production process. That is to say, what
was originally waste is reused, giving it a
new value and avoiding its final disposal
as waste.
(EN2) Percentage of materials used that are recycled input materials. Since 2009, the Andina Division uses scrap iron from local suppliers as a valued material. This scrap is obtained from the manufacture of steel elements –such as drums- at factories external to the division, where they are considered as waste. For the division, this supply is used in the cementation process and during 2011 amounted to 440 tons.
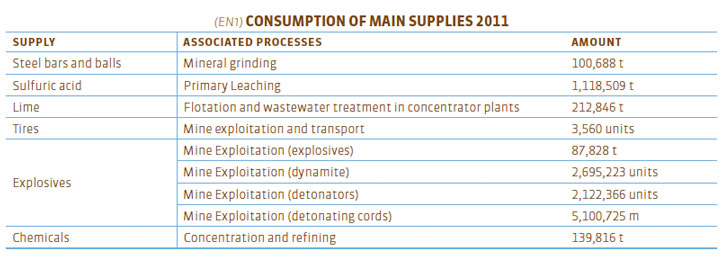
Major supplies
In addition to raw materials and semi-elaborated materials, Codelco uses additional supplies for its productive process. During 2011, we used: